Disclosure of information based on TCFD Recommendations
In April 2022, the FEED ONE Group expressed its support for the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). In alignment with the goals of the Paris Agreement—to keep the global average temperature increase well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels and pursue efforts to limit the increase to 1.5°C—we have actively promoted climate-related disclosures based on the TCFD framework.
Our TCFD report presents scenario-based analysis results in accordance with the four recommended disclosure categories: Governance, Strategy, Risk Management, and Metrics and Targets.
We will continue to enhance the quality and scope of our disclosures while accelerating our efforts to address climate change and achieve sustainable growth for the Group.

Governance
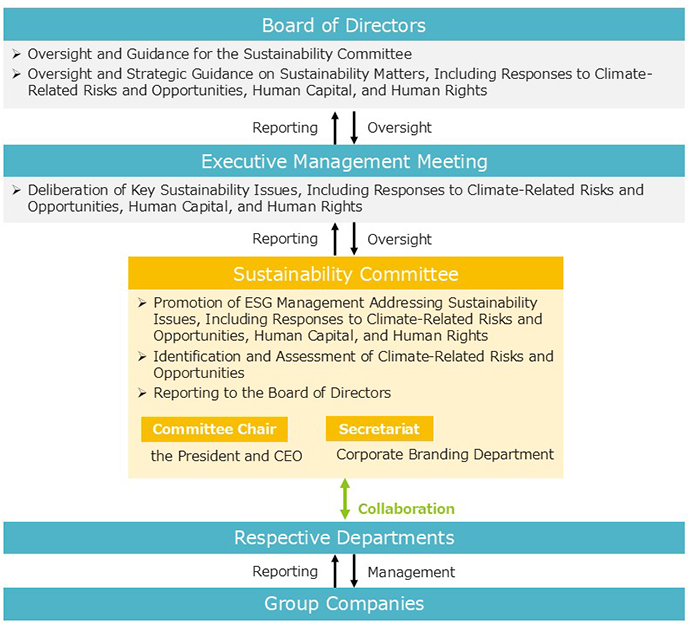
To promote sustainability initiatives, our Group has established the Sustainability Committee. The committee deliberates on key sustainability issues and response measures, including climate-related risks and opportunities, human capital, and human rights. It also supports and advises on the implementation of “One’s Actions,” which are aligned with the medium-term management plan and business strategies, while monitoring progress.
The committee is chaired by the President and CEO, and its members are selected from the heads of business divisions, administrative departments, and the President’s direct reporting units, forming a cross-functional governance structure. The Board of Directors receives regular reports from the Sustainability Committee on sustainability matters—including climate-related risks and opportunities, human capital, and human rights—and provides oversight and strategic guidance on these initiatives.
Strategy
The FEED ONE Group recognizes climate change as a critical management issue. To assess its potential financial impact, we conducted a scenario analysis for the year 2030. This analysis references multiple scenarios published by authoritative bodies such as the International Energy Agency (IEA) and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
●Climate-Related Scenarios at FEED ONE Group
| Classification | Scenario overview | Main referenced scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| 1.5°C and well-below 2°C scenario |
A scenario in which policies and regulations are implemented toward achieving a decarbonized society, and the global temperature will be controlled at around 1.5°C to well-below 2°C above the pre-industrial levels | ・IEA WEO2024 NZE ・IEA WEO2024 APS ・IPCC SSP 1-2.6 ・IPCC RCP2.6 |
| The 4°C Scenario | A scenario in which no new policies and regulations are introduced to address climate changes, and the global temperature will rise about 4°C above the pre-industrial levels | ・IEA WEO2024「STEPS」 ・IPCC SSP 5-8.5 ・IPCC RCP8.5 |
●Results of scenario analysis and relevant measures
| Magnitude of financial impact | High: Impact on profit and loss is over 500 million yen or a material impact on business operation Moderate: Impact on profit and loss is over 100 million yen but 500 million yen or less or a somewhat significant impact on business operation Low : Impact on earnings is 100 million yen or less |
|---|---|
| Timeframe | Short : Within 5 years Medium: Over 5 years but within 10 years Long : Over 10 years |
| Category | Risks and Opportunities | Financial Impact Level | Time Horizon | Response Measures | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5℃/2℃ | 4℃ | |||||
| Transition Risk |
Policy and regulation | Increased Costs Due to Strengthened Regulations on Greenhouse Gas Emissions | High | High | Short-Term | ■Initiatives to Reduce CO2 Emissions (Scope 1 and 2) <Reduction Target> Reduce CO2 emissions by 50% by FY2030 compared to FY2020 levels <Reduction Measures> ・Improve energy intensity through energy-saving activities (e.g., productivity enhancement) ・Enhance energy efficiency by expanding the introduction of energy-saving equipment ・Increase adoption of renewable electricity ・Consider installation of solar power systems at factories and business sites ・Restructure aging factories ・Promote activities to generate J-Credits within the supply chain ■ Initiatives to Mitigate Carbon Tax Impact Across the Supply Chain <Livestock Feed Business> ・Promote bulk delivery of compound feed ・Reduce labor for dismantling transbags at factories <Aquaculture Feed Business> ・Consider using feed bags made from recycled plastic-blended polybags <Food Business> ・Maximize logistics and loading efficiency through centralized delivery to distribution centers ・Continue promoting the use of molded pulp packs for commercial egg products ・Reduce the use of plastic packaging materials in meat processing operations |
| Reputation | Decline in Corporate Reputation Due to Inadequate Climate Change Response and Disclosure | Low | Low | Long-Term | ・Promotion of initiatives to achieve CO2 emissions reduction targets ・Contribution to overall societal CO2 reduction through food recycling and reduction of food loss ・Enhancement of climate-related disclosures and transparency |
|
| Physical Risk | Acute | Physical damage to livestock barns and aquaculture pens caused by natural disasters, and reduced feed sales volume due to disruptions in logistics | Low | Low | Short-Term | ■Response to Producers <Livestock Feed Business> ・Provide information related to livestock facility equipment and strengthen collaboration with local governments and producers. ・Establish a system that enables timely supply of necessary support in the event of a disaster. <Aquaculture Feed Business> ・Collect and provide information on advanced overseas aquaculture facilities that can withstand wave action. ・Develop feed compatible with such facilities to build a support system for aquaculture operations. ■Measures Against Logistics Disruptions ・Continue training and response activities based on the existing Business Continuity Plan (BCP). ・Ensure a stable supply system by establishing a structure that enables alternative delivery through multiple distribution routes. |
| Suspension of factory operations due to natural disasters | Low | Low | Short-Term | ・Ensure employee safety and protect feed manufacturing and sales operations through training and response activities based on the Business Continuity Plan (BCP). ・Minimize risks in the event of factory damage by securing production support from unaffected factories. |
||
| Chronic | The rise in air and sea temperatures may affect livestock and farmed fish, leading to changes in suitable production areas. As a result, feed sales volumes may decline due to reduced demand in previously productive regions. |
Low | Medium | Long-Term | ■Support for Producers <Livestock Feed Business> ・Contribute to improving livestock productivity by collecting and sharing information on breeding improvements and technologies such as stable air conditioning systems for barns. <Aquaculture Feed Business> ・Develop products compatible with land-based recirculating aquaculture systems, in response to growing demand for farming methods less affected by environmental changes. |
|
| Climate change may lead to reduced raw material production and increased prices, resulting in a decline in profitability | High | High | Long-Term | ■Use of Cost-Effective and High-Quality Raw Materials <Livestock Feed Business> ・Diversify import sources to reduce risks related to procurement and price fluctuations. ・Promote the use of domestically produced raw materials as alternatives to imported ones. <Aquaculture Feed Business> ・Monitor supply conditions and strengthen collaboration with domestic and local fishmeal producers to enable flexible responses. ・Promote the shift to low-fishmeal and fishmeal-free feeds, which are in growing demand due to concerns over resource depletion and rising prices. ■Appropriate Price Adjustments <Livestock Feed Business> ・Continue quarterly price revisions based on raw material trends. ・Maintain price adjustments for processing fees in response to rising energy costs. <Aquaculture Feed Business> ・Although price revisions are irregular, adjust sales prices in response to raw material cost fluctuations to reduce risk. |
||
| Opportunities | Resource Efficiency | Reduction of energy consumption through improved manufacturing efficiency | Low | Low | Short-Term | ■Initiatives using IoT ・Visualizing energy usage by monitoring electricity and steam consumption by process and managing operating equipment appropriately to reduce energy consumption. ■Initiatives to improve manufacturing efficiency ・Improving manufacturing efficiency by consolidating product types and raw materials and reviewing pellet sizes in aquaculture feed. |
| Reduction of logistics costs through the development of efficient distribution processes in raw material procurement | Low | Low | Short-Term | ■Raw material initiatives ・Promote procurement of raw materials from locations closer to factories. ・Encourage a shift from long-distance truck transportation to coastal shipping |
||
| Products and services | Increase in feed sales volume through the development and sale of sustainable feed and the use of sustainable raw materials | Medium | Medium | Short-Term | ■Livestock feed business ・Continue developing and selling products that improve feed conversion ratios and reduce manure volume. ・Continue efforts to develop feed that reduces methane emissions from cattle. ・Expand feed sales by leading product development through ongoing global sourcing and information gathering. ■Aquaculture feed business ・Increase sales volume through low-fishmeal and fishmeal-free feed that does not rely on natural resources. ・Lead efforts to utilize and commercialize insect-based ingredients, algae, and methanotrophs—despite challenges such as limited supply and high cost—and gain formulation expertise to expand feed sales. |
|
| Increase in feed sales volume through improved heat stress mitigation technologies in livestock production | Medium | Medium | Short-Term | Contributing to improved livestock productivity through continued development and sales of heat stress mitigation feed and supplements, ongoing research and development, and continuous information gathering on livestock management technologies to provide high-quality, environmentally conscious services | ||
| Market | Increase in feed sales volume through the expansion of land-based recirculating aquaculture systems unaffected by rising sea temperatures | Low | Low | Short-Term | Expansion of feed sales volume in new markets through the advanced development of feed technologies that meet new performance requirements in recirculating land-based aquaculture, such as water quality management and waste reduction, which were not issues in traditional farming methods | |
●Impact of a Carbon Tax Introduction
We examined the following two patterns based on the Scope 1 and Scope 2 CO2 emissions from our company and consolidated subsidiaries, including feed manufacturing plants and food and farm-related subsidiaries.
In the 1.5°C scenario, if our group takes no action to reduce CO2 emissions and emissions increase in line with business growth, the estimated carbon tax in FY2030 would be approximately 1.1 billion yen.
On the other hand, if our group achieves its CO2 reduction target of 50% by FY2030 compared to FY2020, the carbon tax could be reduced by approximately 600 million yen, resulting in a total of around 500 million yen.
Please note that the cost of achieving CO2 reductions is not included in this estimate.
<Carbon tax amount and calculation method for our group in the 1.5°C scenario in FY2030>
(ⅰ) If our group takes no action to reduce CO2 emissions
(ⅱ) If our group reduces CO2 emissions by 50% by FY2030 compared to FY2020
b. If the Group reduced CO2 emissions by 50% in FY2030 (vs. FY2020)
| Impact amount | Calculation method | |
|---|---|---|
| (ⅰ) | 1,103 | Calculated by multiplying the projected CO2 emissions in FY2030, adjusted for business growth rate, by the carbon tax※ |
| (ⅱ) | 486 | Calculated by multiplying the projected CO2 emissions in FY2030, adjusted for business growth and assuming a 50% reduction compared to FY2020, by the carbon tax※ |
- ※Carbon tax under the 1.5°C scenario: FY2030 – $140/t-CO2 (based on IEA WEO 2024 NZE for advanced economies)
Exchange rate used for calculation: 149 yen per US dollar (as of March 31, 2025)
Calculated at 150 yen to the US dollar
Risk Management
- 1Process for identifying and assessing climate-related risks
Through discussions with relevant departments within our group, the Corporate Planning Department, which oversees risk management, takes the lead in identifying climate-related risks and opportunities by considering both internal and external factors.
The identified risks and opportunities are analyzed and evaluated both quantitatively and qualitatively using the systems and indicators defined in our Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) regulations, and appropriate response measures are formulated. - 2Process for managing climate-related risks
The Sustainability Committee monitors the implementation status of responses to climate-related risks and opportunities, verifies the validity of these measures, and works to improve them.
Important matters are reported to the Management Committee and the Board of Directors.
The Board of Directors supervises and advises on the response measures reported by the Sustainability Committee. - 3 Integration of climate-related risk processes into overall risk management
Climate-related risks are managed in coordination with the company-wide RM (Risk Management) meetings, aiming to minimize risks and maximize opportunities across the entire group.
Metrics and Targets
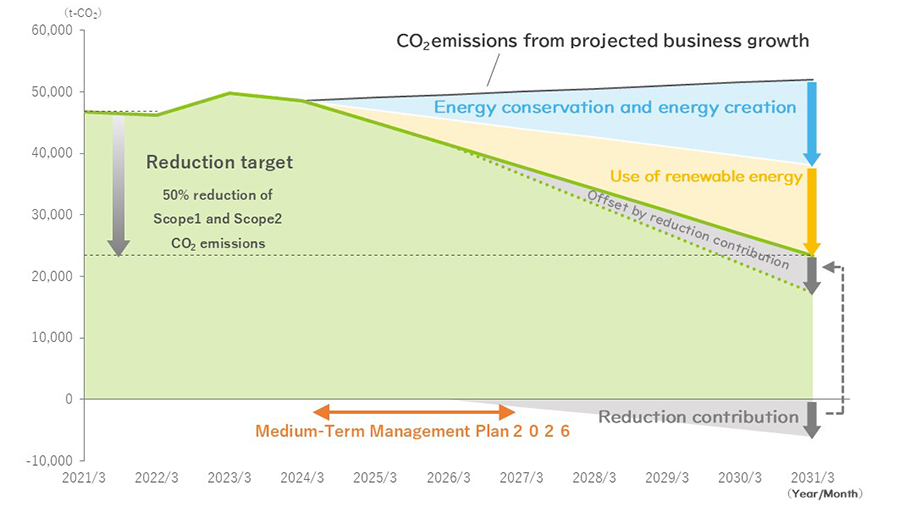
The FEED ONE Group has set CO2 emissions as key metrics to minimize risks and maximize opportunities related to climate change, and set the medium-term to long-term targets for FY2030 and FY2050.
We have formulated the following three reduction measures to achieve our medium-term targets: (1) energy-saving and energy-generating activities, (2) switch to renewable energy electricity, and (3) carbon offsets with avoided emissions. We then prepared a decarbonization roadmap by taking account of increased emissions due to business growth until the target fiscal year of 2030.
Medium-term targets (FY2030) : Scopes 1 and 2 CO2 emissions 50% reduction vs. FY2020 levels
Long-term targets (FY2050) : Achieve carbon neutrality in entire supply chains
< CO2 Emission Results >
Unit:t-CO2
| Item | Target scope | FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | FY2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scope1・2 | Total | 46,626 | 46,267 | 49,546 | 48,412 | 44,331 |
| Scope1 | FEED ONE | 6,226 | 7,727 | 11,221 | 10,039 | 9,687 |
| FEED ONE and subsidiaries※1 | 10,167 | 9,626 | 9,462 | 9,007 | 8,951 | |
| subtotal | 16,393 | 17,353 | 20,684 | 19,046 | 18,638 | |
| Scope2 | FEED ONE | 14,910 | 14,938 | 14,964 | 14,333 | 9,965 |
| FEED ONE and subsidiaries※1 | 15,323 | 13,975 | 13,898 | 15,033 | 15,728 | |
| Subtotal | 30,233 | 28,913 | 28,862 | 29,366 | 25,693 | |
| Scope3 | Total | 1,433,714 | 1,634,175 | 1,730,980 | 1,737,428 | 1,724,834 |
| ①Purchased goods and services※2 | FEED ONE and subsidiaries※1 | 1,391,146 | 1,611,030 | 1,712,159 | 1,717,291 | 1,695,577 |
| ②Capital goods※2 | FEED ONE and subsidiaries※1 | 29,172 | 10,375 | 7,581 | 9,918 | 14,453 |
| ③Fuel-and energy-related activities not included in Scope1 or 2※2 |
FEED ONE and subsidiaries※1 | 6,625 | 6,363 | 4,602 | 4,728 | 9,268 |
| ⑤ Waste generated in operations | FEED ONE(factories and Research & Development Center) and subsidiaries※1 | 953 | 1,047 | 950 | 944 | 1,122 |
| ⑥Business travel | FEED ONE(Head Office) | 71 | 78 | 104 | 162 | 183 |
| ⑦Employee commuting | FEED ONE | 336 | 359 | 346 | 346 | 360 |
| ⑧Upstream leased assets | - | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| ➉Processing of sold products | - | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| ⑪Use of sold products | - | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| ⑫End-of-life treatment of sold products | FEED ONE | 854 | 842 | 862 | 897 | 819 |
| ⑬Downstream leased assets | FEED ONE | 4,558 | 4,081 | 4,375 | 3,142 | 3,045 |
| ⑭Franchises | - | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| ⑮Investments | - | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
- Note 1: Consolidated subsidiaries (feed manufacturing plants and food/farm subsidiaries)
- Note 2: The aggregation criteria were revised starting from FY2024. Figures for FY2023 and earlier were calculated based on the previous criteria.
- Remark : Due to rounding, totals may not match exactly.
< decarbonization roadmap >
< CO2Emission Reduction Efforts >

- Location
Kitakyushu Aquaculture Feed Plant
- Start date
April 2024
- Purpose and overview
To reduce CO2 emissions associated with electricity use, 100% of the electricity used at this plant has been switched to renewable energy sources.
This enables the procurement of clean electricity with low environmental impact.

- Location
Kitakyushu Livestock Feed Plant
- Start date
July 2024
- Purpose and overview
To reduce CO2 emissions associated with fuel use, electric forklifts equipped with lithium-ion batteries have been introduced.
Compared to conventional diesel forklifts, these models maintain high performance while achieving lower CO2 emissions and reduced operating costs.
- Methodology ID
AG-005
- Methodology name
Extension of mid-season drainage period in rice cultivation
- Purpose and overview
To offset CO2 emissions from our group, we launched a J-Credit creation project
targeting feed rice producers who are our business
partners, with our company acting as the project operator and manager.
The feed rice produced is used as a raw material in our compound feed,
contributing to greenhouse gas reduction across the supply chain.
In FY2024, we received certification for 1,582 t-CO2 in credits. These
credits are planned to be used to offset our group’s emissions.
